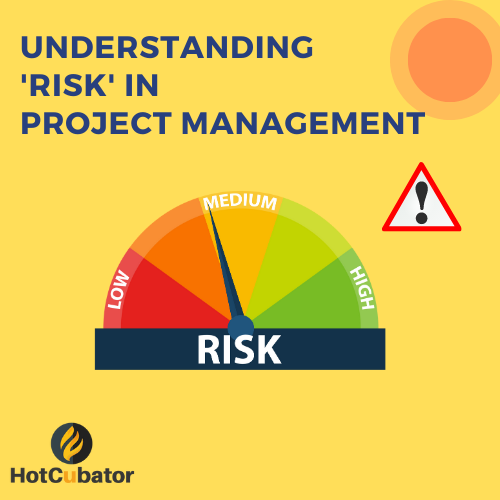
One of the obvious phenomena in Project Management is risk. Risk is crucial in project management because every project is inherently uncertain and carries a degree of risk. Risk can be defined as the potential for an event or circumstance to have a negative impact on the project’s objectives, such as delays, increased costs, or decreased quality.
Managing risks in project management is important because it enables project managers to identify potential problems before they occur and develop strategies to mitigate them. This can help to ensure that the project is completed successfully, on time, and within budget.
By identifying and addressing risks early on, project managers can avoid costly delays and unforeseen expenses, which can lead to project failure. Risk management also helps project managers to anticipate and prepare for potential challenges, which can increase the chances of project success.
Furthermore, risk management helps project teams to prioritize tasks and allocate resources effectively. By focusing on the most significant risks, project teams can ensure that their efforts are aligned with the project’s objectives and minimize the likelihood of unexpected problems. This ultimately increases the chances of project success and helps to deliver projects that meet or exceed stakeholder expectations.
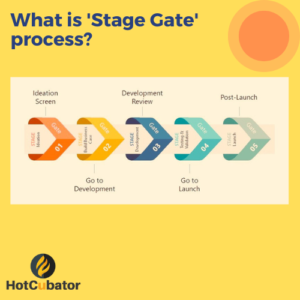
Steps of risk management in Project Management:
There are several steps in risk management which helps to effectively manage risk in project management, minimize the likelihood of potential risks, and ensure the project’s success:
- Identify Risks: Begin by identifying potential risks that could impact the project. This can be done by brainstorming with team members, reviewing historical data from similar projects, and analyzing external factors that could affect the project.
- Assess Risks: Once you’ve identified potential risks, evaluate their likelihood of occurring and the potential impact on the project. You can use a risk assessment matrix to help prioritize the risks based on their severity.
- Develop a Risk Management Plan: Develop a plan that outlines how you will manage each risk. The plan should include specific actions that will be taken to mitigate each risk, such as developing contingency plans, establishing communication protocols, or allocating additional resources.
- Monitor and Control Risks: Keep a watchful eye on the identified risks and be prepared to adjust your plans if necessary. Continuously monitor the project’s progress and any changes in the external environment that could impact the risks.
- Communicate Risks: Communicate risks to all stakeholders and team members. Keep everyone informed about the identified risks, the potential impacts, and the mitigation strategies in place. This can help to minimize surprises and maintain stakeholder support.
- Review and Evaluate: Regularly review and evaluate the effectiveness of your risk management plan. Use lessons learned from previous projects to identify any areas for improvement and make adjustments accordingly.
Risk management approaches:
So there are several ways risk can be management The risk management approaches may vary depending on the nature of the project, however, the type of risk, and the organization’s risk management culture to a lot extent will determine what specific risk management approach is current.
- Avoidance: This approach involves eliminating the risk altogether by avoiding the activities or situations that could cause the risk to occur. This is often the best approach for high-risk activities or situations that could have severe consequences.
- Mitigation: This approach involves reducing the probability or impact of a risk by taking specific actions to address it. For example, adding additional resources or changing project plans to reduce the likelihood of a risk occurring.
- Transfer: This approach involves transferring the risk to a third party, such as an insurance company. This is often used for risks that are beyond the project team’s control, such as natural disasters.
- Acceptance: This approach involves accepting the risk and developing a plan to minimize its impact if it occurs. This is often used for risks that have a low probability or low impact.
- Exploitation: This approach involves taking advantage of positive risks or opportunities that arise during the project. For example, if a supplier unexpectedly offers a lower price, the project team may choose to exploit this opportunity.
- Sharing: This approach involves sharing the risk with other stakeholders or team members. For example, if a risk impacts multiple departments within an organization, the risk may be shared across those departments.
Tools to be used for project risk management:
Although risks are almost unavoidable, but as a project manager you should be familiar with a variety of risk management tools to use on regular basis to ‘risk-proof’ your projects. Here are the most commonly used tools for risk management:
- Risk register: A risk register is a document that lists all the identified risks, along with their probability, impact, and the actions taken to mitigate them.
- Risk assessment matrix: A risk assessment matrix is a tool that helps project managers prioritize risks based on their probability and impact. It usually consists of a table with probability and impact ratings that are assigned to each risk.
- SWOT analysis: A SWOT analysis is a technique used to identify and analyze the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with a project. It helps project managers to assess the overall risk profile of the project.
- Risk categorization: Risk categorization is a process of grouping similar risks together based on their characteristics. This helps project managers to develop targeted risk management strategies for each category of risk.
- Monte Carlo simulation: Monte Carlo simulation is a statistical technique that is used to model the impact of risk and uncertainty on project outcomes. It involves running thousands of simulations to determine the probability of different outcomes.
- Risk response planning: Risk response planning involves developing strategies to mitigate, avoid, transfer, or accept risks. It helps project managers to develop a proactive approach to risk management.
- Contingency planning: Contingency planning involves developing a plan for responding to unexpected events or risks. It helps project managers to be prepared for unexpected events and to minimize their impact on the project.
No matter how much you try, risk will likely occur in programs and projects. But a savvy project or program manager will always take a stock take of risks well in advance to make sure that there remain appropriate strategies to defend against risks.